Bit Shift Cipher
A simple encryption technique that operates on the binary representation.
What is the Bit Shift cipher?
The Bitshift Cipher is a type of substitution cipher, as each character in the plaintext is replaced with a different character based on its binary representation.
Plain Text
Decrypt
Key
Cipher Text
How does the Bit Shift cipher work?
The Bitshift Cipher works by shifting over the bits of the text's ASCII using the bitwise << operator. To encode the text, the cipher loops through the text, and for each character, it loops through the key array and shifts the bits a certain number of places based on the current key character. The maximum shift is limited using modulo to avoid having a bit shifted by hundreds of places. After each character is encoded, it is added to an array, and the key is reversed to make frequency analysis harder.
To decode, the cipher reverses the key and loops through the text and key, shifting the bits back to their original position based on the current key character. The key can be as long as you want, making brute force harder, and reversing the key makes frequency analysis hard. However, different programming languages may have different outputs depending on the base64 support.
The bit shift cipher is a very basic encryption technique and is not considered to be secure, as it can easily be broken with simple techniques like frequency analysis. However, it can be a useful tool for teaching basic encryption principles and for encoding messages that do not require high levels of security.
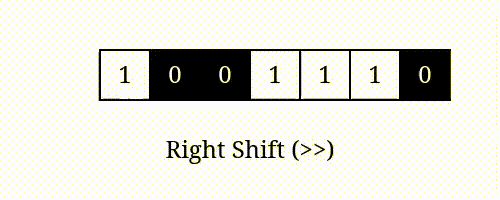
Visualizing the Bit Shift cipher
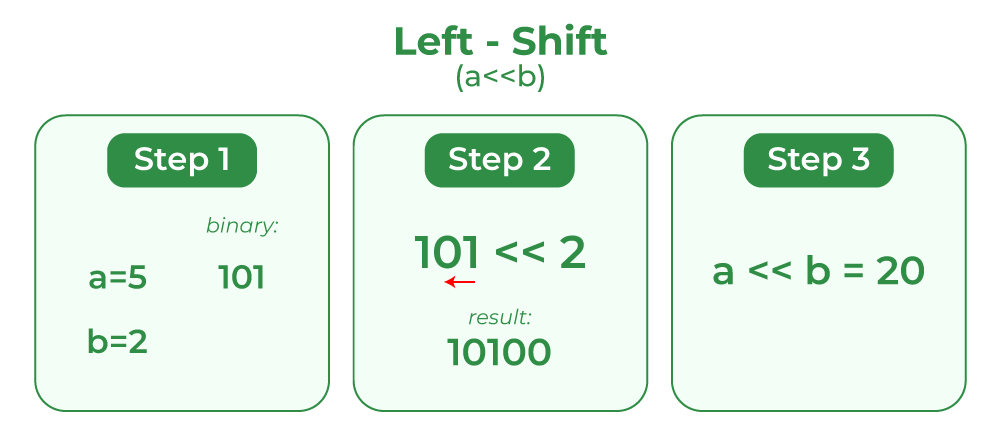
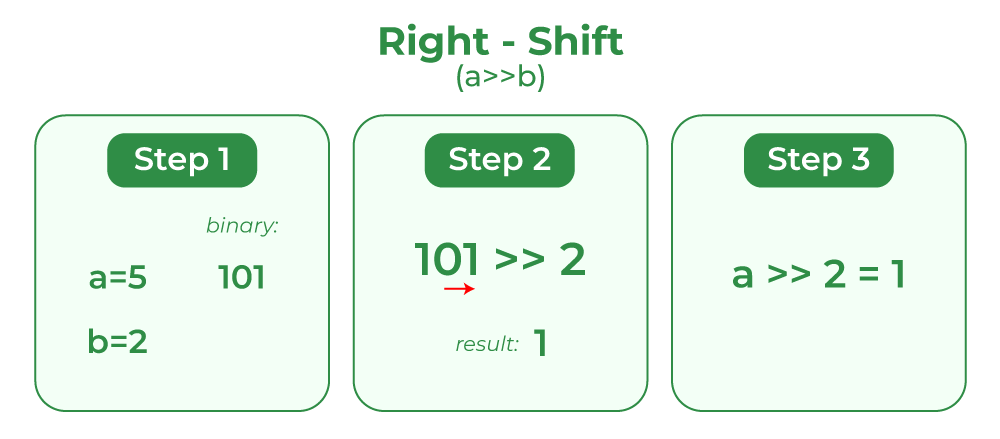
History
The history of the Bit shift cipher can be traced back to the early days of computing. In the 1950s and 1960s, computers were large, expensive machines that were primarily used for scientific and military applications. At the time, encryption was primarily done using mechanical devices, such as the Enigma machine used by the Germans during World War II. However, as computers became more powerful and more widely available, researchers began to explore new ways of encrypting data. One of the earliest methods to emerge was the Bit shift cipher. This method is based on the concept of shifting the bits of the plaintext to produce the ciphertext.
The Bit shift cipher was first described in detail in the late 1970s by a group of researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The researchers were working on a system for encrypting data on computer networks, and they developed the Bit shift cipher as part of this effort. Since then, the Bit shift cipher has been used in a wide variety of applications, including computer programming, cryptography, and digital signal processing. It is a simple but effective encryption method that can be implemented quickly and easily in software, making it a popular choice for many applications.
One of the strengths of the Bit shift cipher is its flexibility. The key used in the encryption process can be of any length, and the plaintext can be of any size. This makes it easy to customize the encryption method to suit the needs of a particular application. However, the Bit shift cipher is not without its weaknesses. One of the main vulnerabilities is that it is vulnerable to brute-force attacks. Because the key is relatively short and the encryption method is relatively simple, it is possible for an attacker to try all possible keys until the correct one is found.
